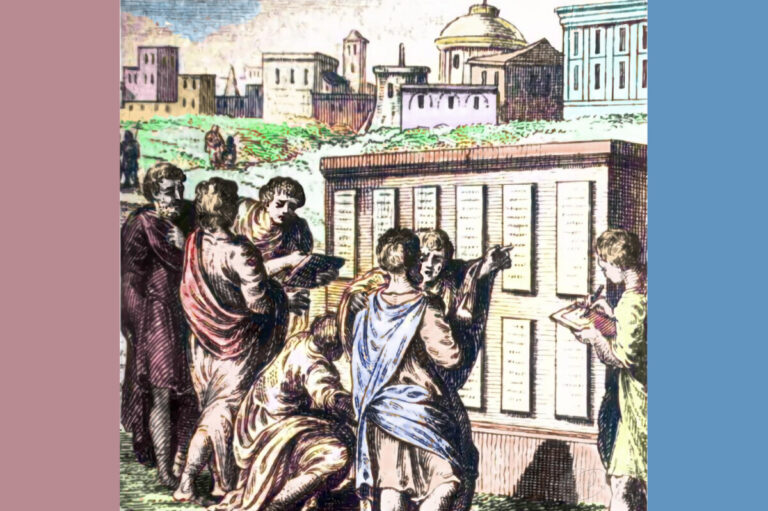
The Twelve Tables were rules citizens had to follow, and limits on the powers of the government. This idea was used several times during Roman history to force the Patricians, aristocrats, to consider the views of the plebeian citizens, commoners. In 451 BCE, plebeians went on strike to protest the tyranny of magistrates. The Twelve Tables came out of that strike. These bronze tablets were set up in the Forum of Rome for all citizens to see and students to study.
Content examples:
- Table I – when a person is accused of something, both accused and accuser must be present at a trial. If only one party shows up, the judge is free to rule in their favor.
- Table III – debtors have 30 days to pay off a debt. After that, a creditor is free to imprison them.
- Table IV – approval to put to death a dreadfully deformed child.
- Table V – all women, except Vestals (virgin priestesses), must have a guardian regardless of age. The guardian had no say in her private matters, but did guide her public matters especially matters of money.
- Table VI – a man’s will is binding.
- Table VIII – lists specific punishments for specific crimes. And, a person who fails to show up as a trial witness, can never again be a witness. And, a person shown to have lied in court will be put to death.
- Table IX – judges who have taken a bribe as well as anyone committed of treason will be put to death.
- Table XI – prohibits marriages between plebeian (aristocrats) and patrician (commoners).