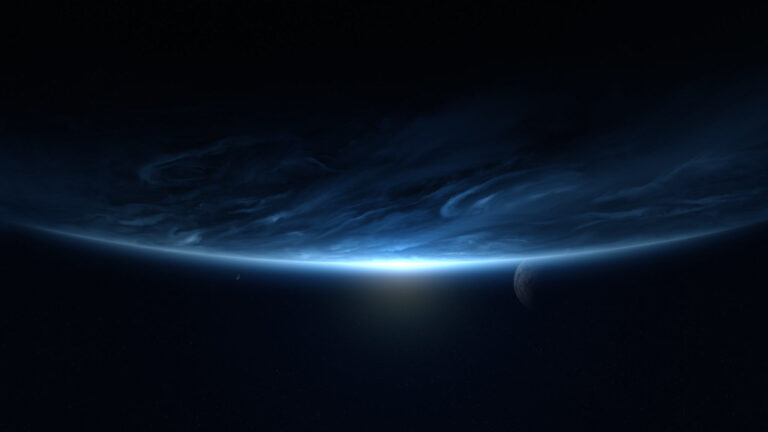
GOE: The Great Oxidation Event started enriching the atmosphere with oxygen beginning around 2.4 billion years ago. It marked one of Earth’s most dramatic transformations. Initiated by the widespread activity of photosynthetic cyanobacteria, this period, known as the Great Oxidation Event, gradually saw the accumulation of oxygen that was initially absorbed by oceanic iron. As these iron sinks saturated, oxygen spilled into the atmosphere, paving the way for profound environmental and biological changes. The creation of an ozone layer, the oxygenation of the oceans, and the consequent rise of aerobic life forms set the stage for the later explosion of complex life on Earth, fundamentally altering the course of our planet’s history.
Breathable air to animals, including humans, started about 540 million years ago.