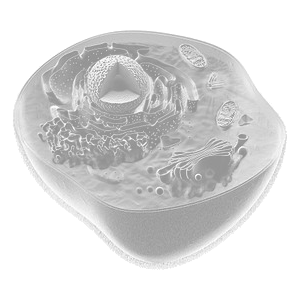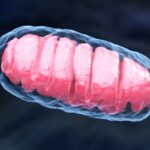
All life today are either Prokaryote or Eukaryote. Around 2 billion years ago, Eukaryotes evolved from Prokaryotes. The evolutionary leap to eukaryotes introduced cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, a complex architecture derived from prokaryotic predecessors through endosymbiosis. This process, crucial for eukaryotic evolution, involved the incorporation of prokaryotic cells into the cytoplasm of early eukaryotes, giving rise to essential organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Mitochondria are a key component of eukaryotic cells, contributing to their ability to generate energy more efficiently than prokaryotic cells
- Domain: Eukaryota > Kingdom: Protista (or ancestral eukaryotes)