World Population: 1.5 Million
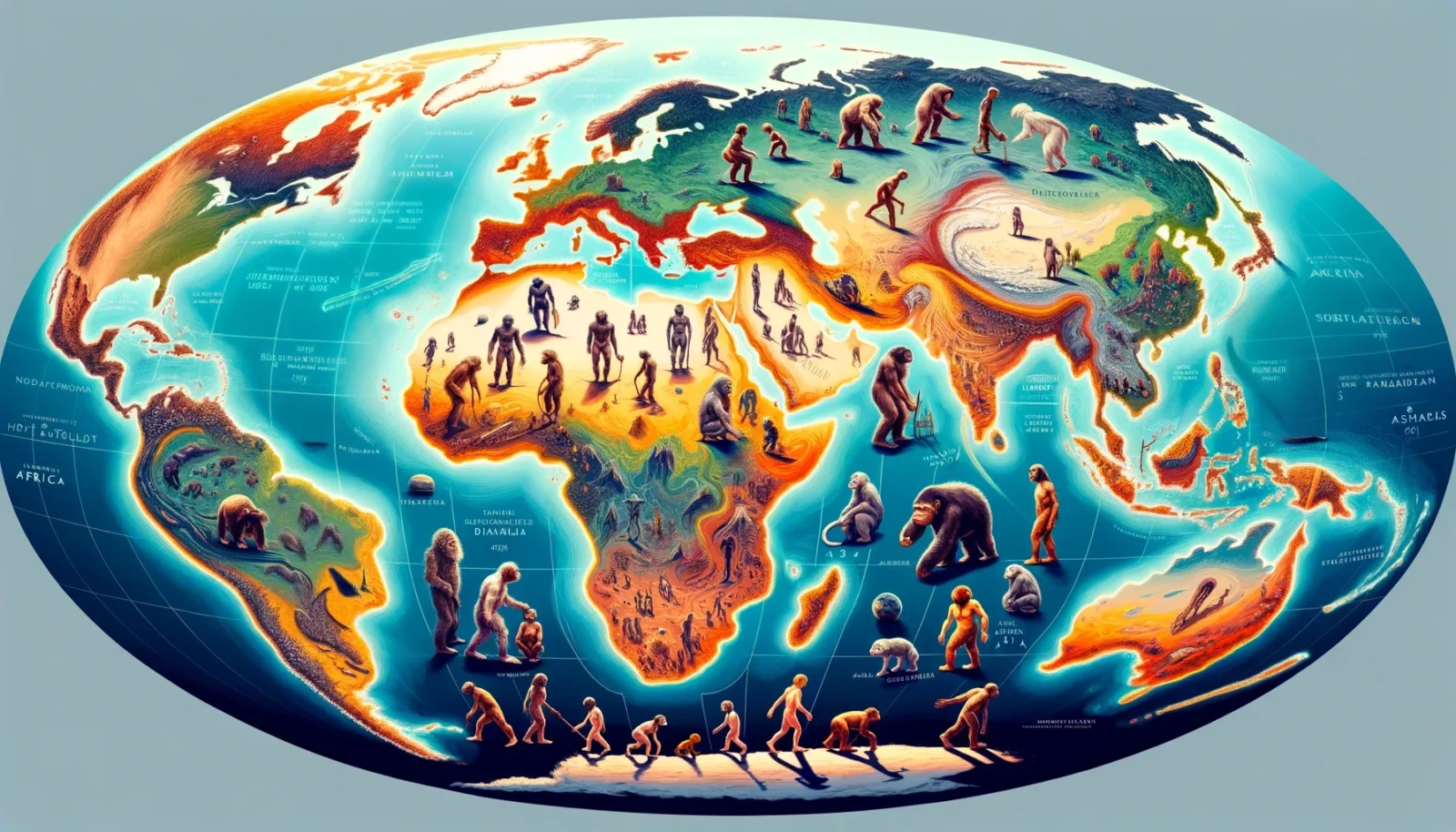
Cognitive Revolution 50,000 BCE – 70,000 BCE. Population range: 500,000 to 2.5 million. Given the uncertainties and lack of direct data, the following are speculative estimates. Africa-Middle East: 50-60% or 600,000 to 1 million people Africa, being the origin of modern humans, likely had the highest population density at this time, particularly in Sub-Saharan regions […]
World Population: 1.5 Million Read More »