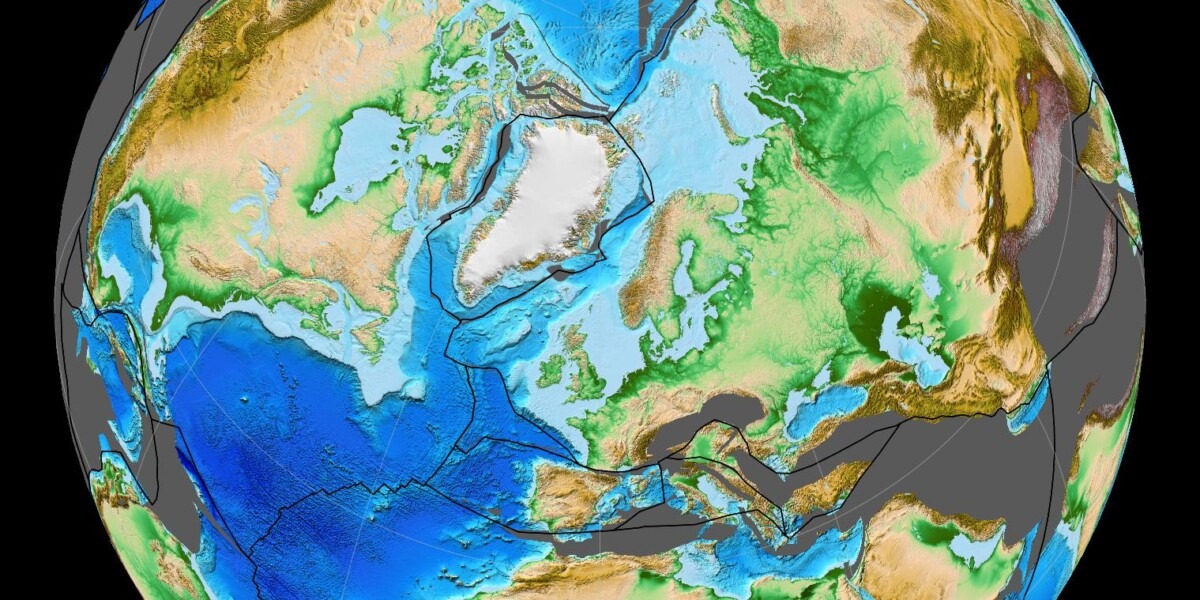
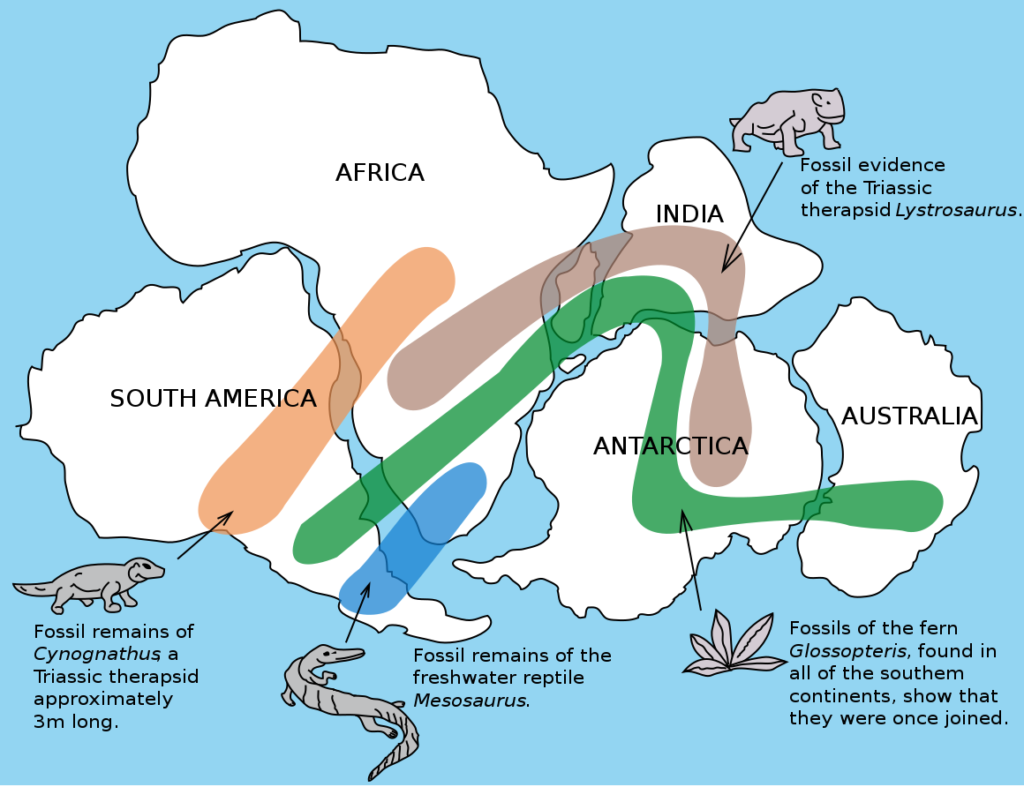
First Atoms
The image of the early universe that we see in the CMB reveals a time shrouded in darkness. During this era, the 17 known particles first started to combine to form the universe’s first atoms. Electrons, protons, and neutrons came together to create neutral hydrogen atoms, a process that allowed photons—or light—to traverse the cosmos […]