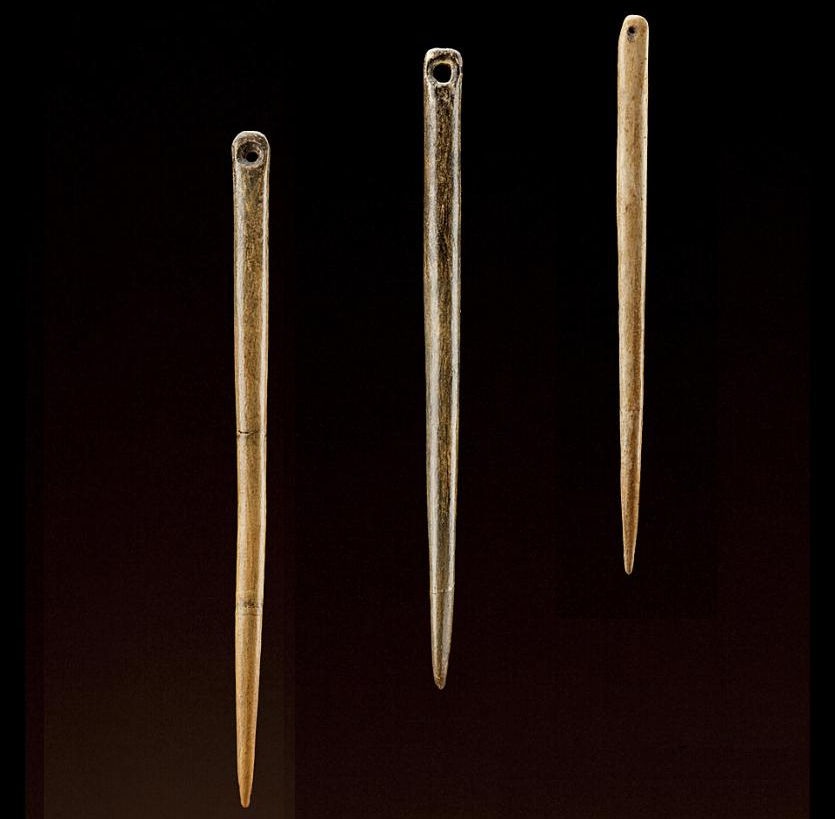
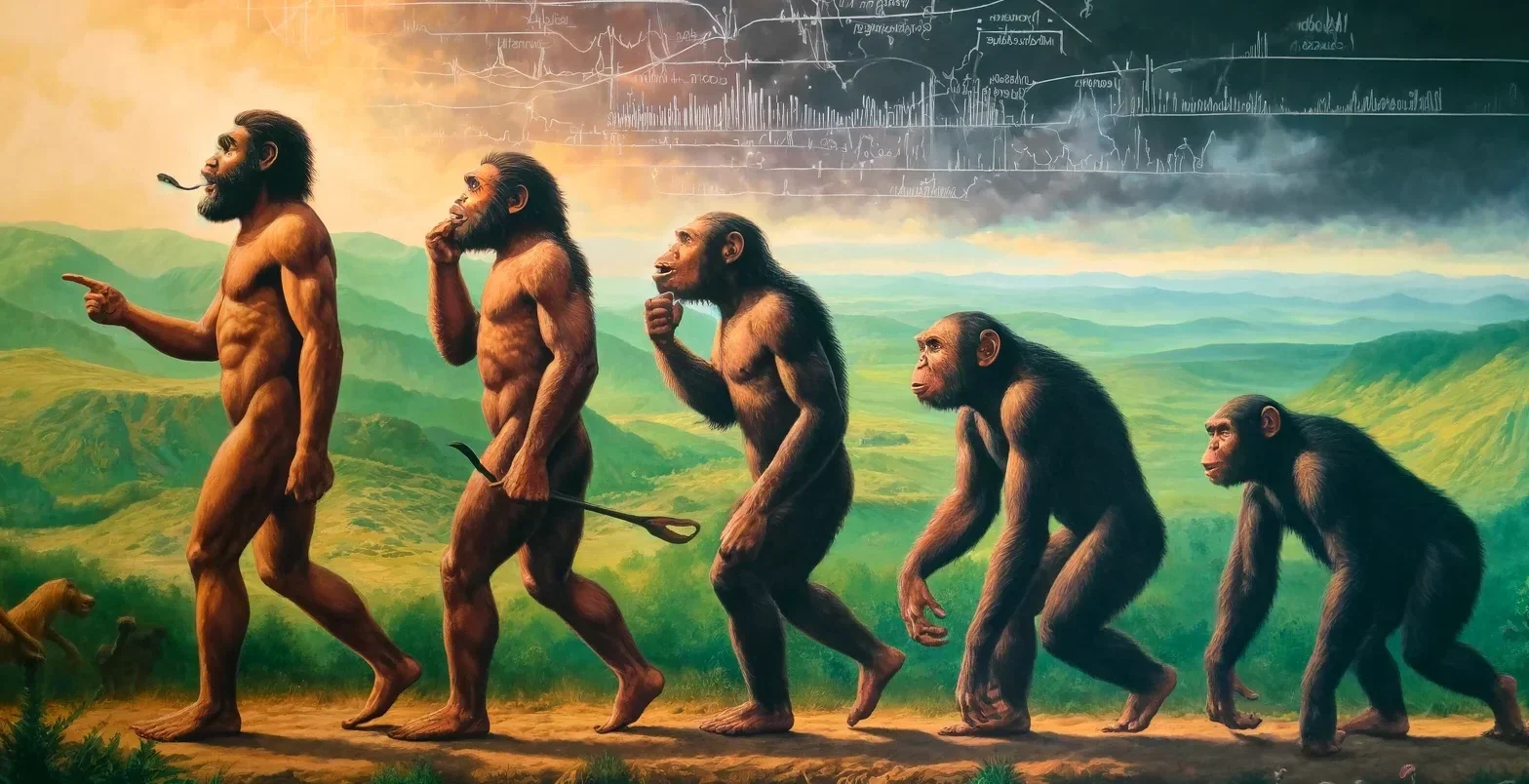
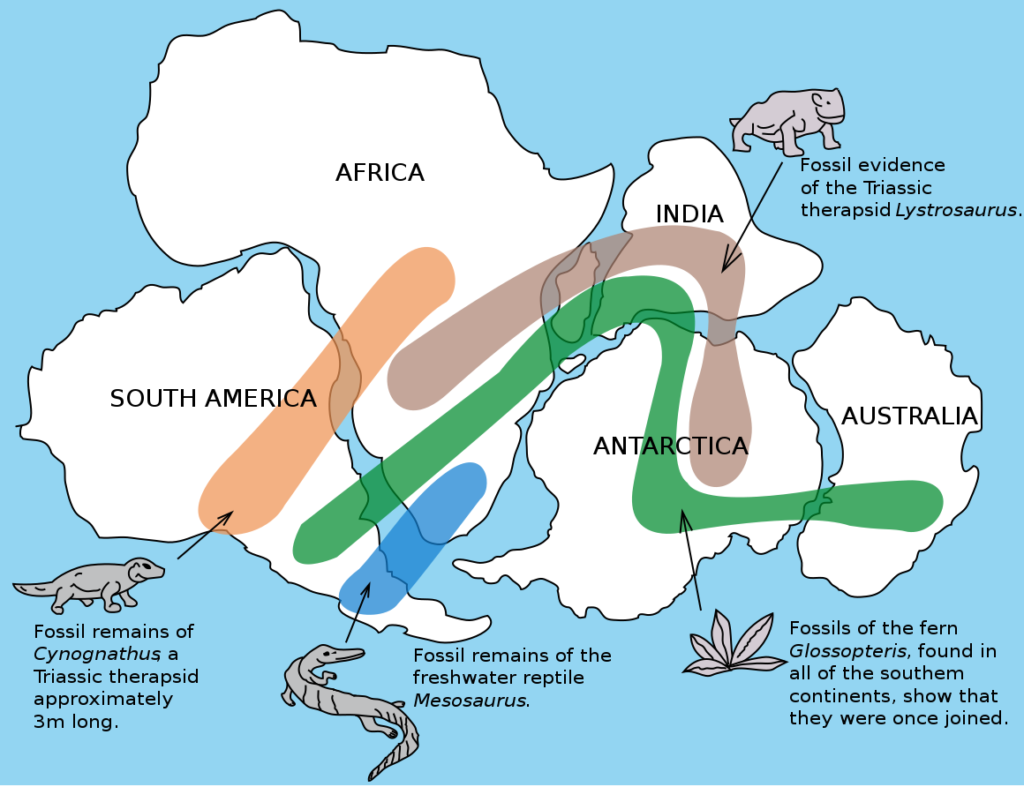
Birth of the Sun
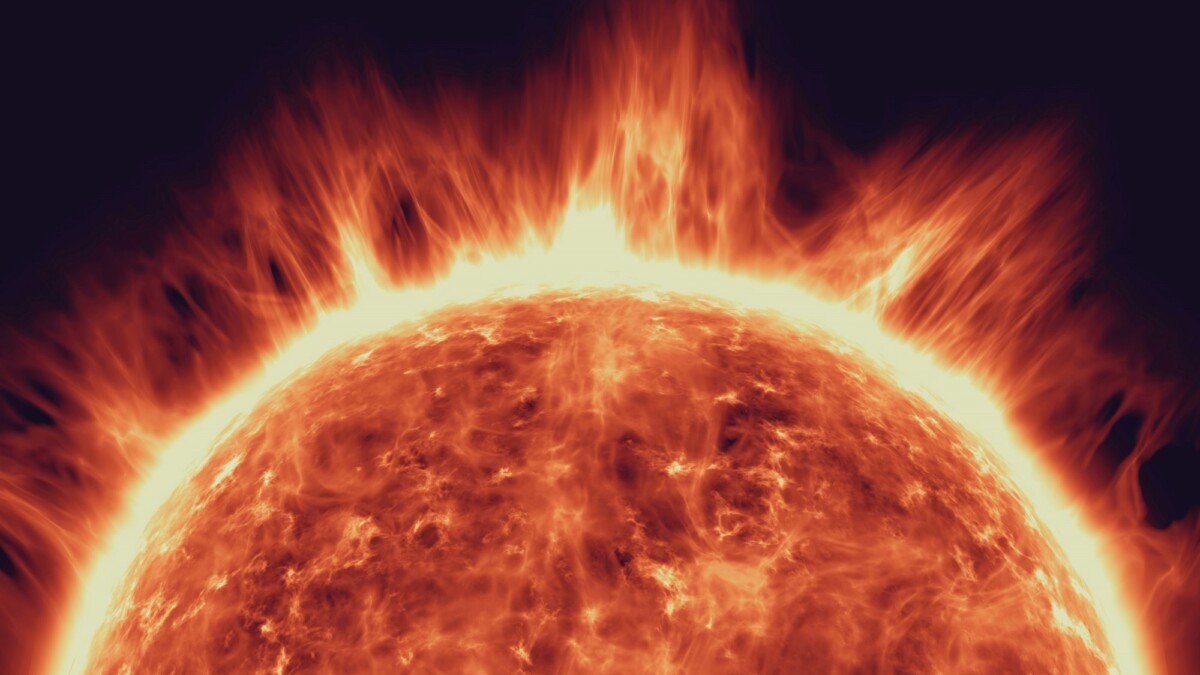
4.6 billion years ago, a cloud of gas and dust collapsed under the force of its own gravity to form our solar system.With the Sun at its center, glowing, the planets had not yet formed. The Sun, a G-type Population 1 star, shines brightly with a surface temperature of about 9,400 degrees, 5,500 Kelvin, and […]