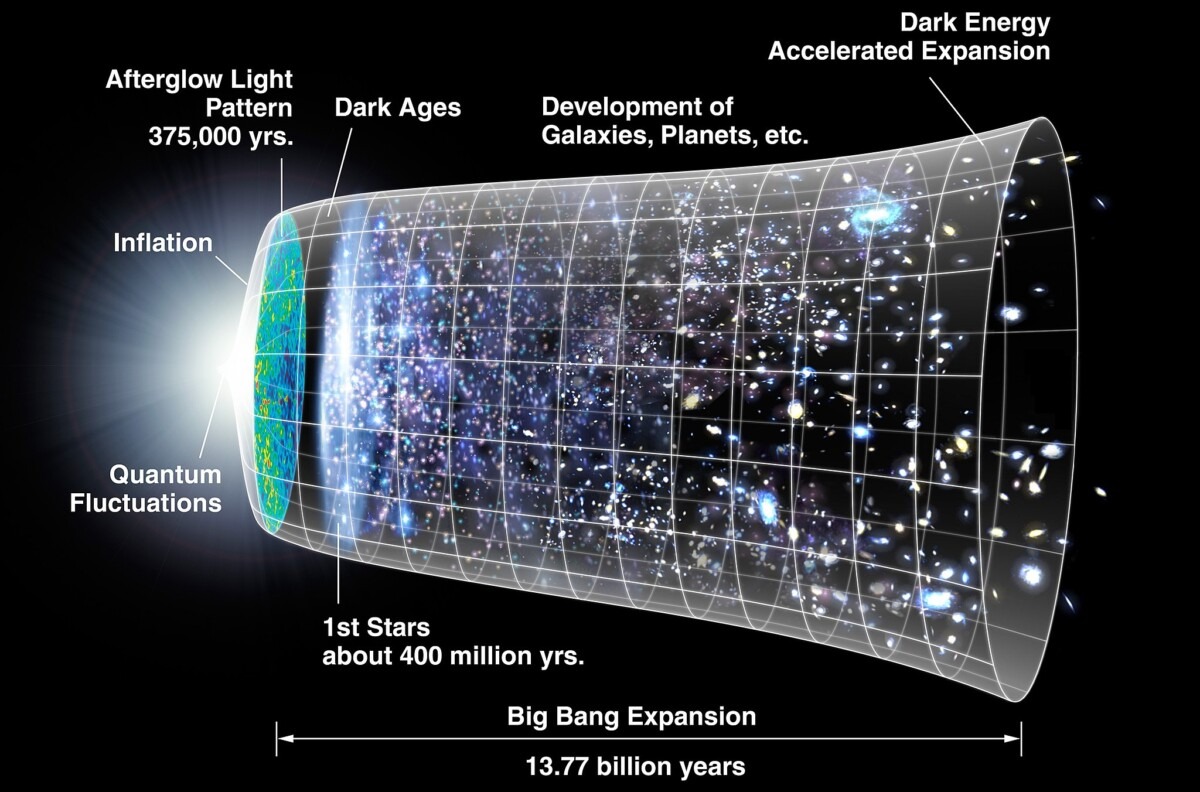
Chocolate
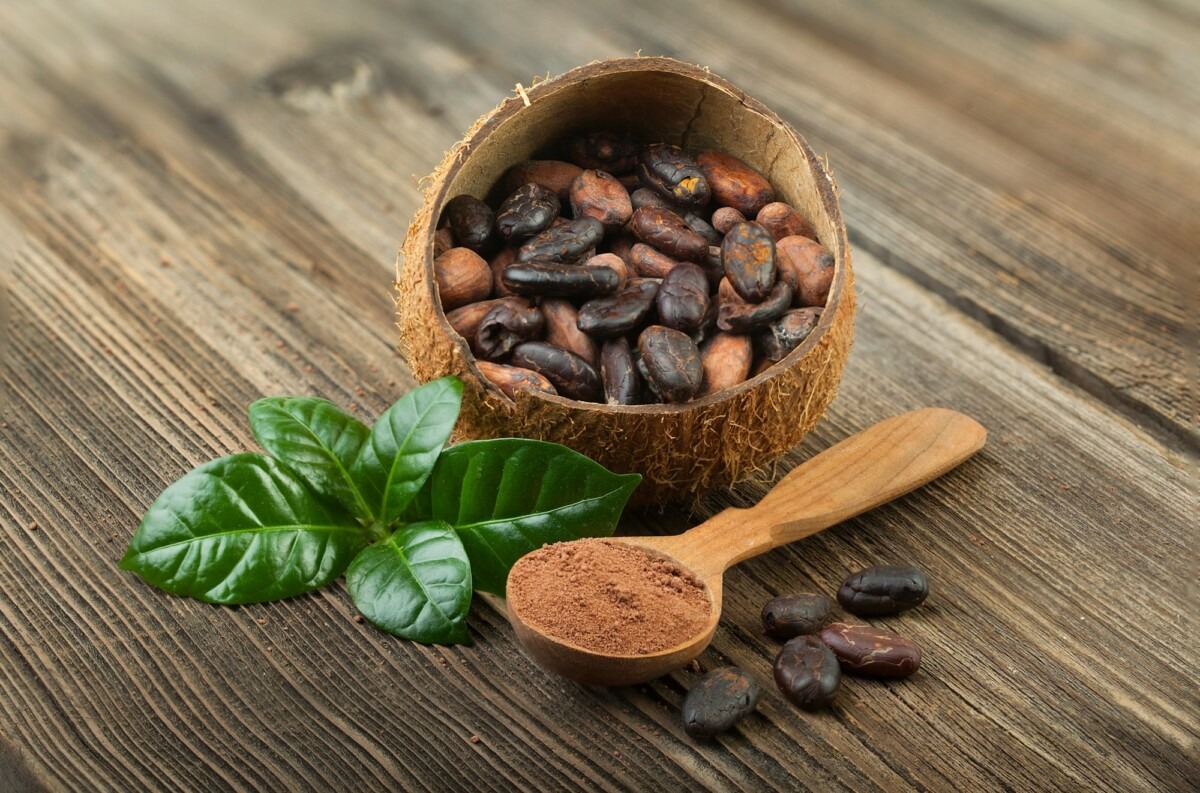
In the tropical rainforests of Mesoamerica, the ancient Olmecs unlock the secrets of the cacao pod. By fermenting, roasting, and grinding the seeds, they create the bitter beverage chocolate. This divine elixir lays the foundation for chocolate’s enduring legacy, cherished by the Mayans and Aztecs as a ceremonial drink, a currency, and a medicine.