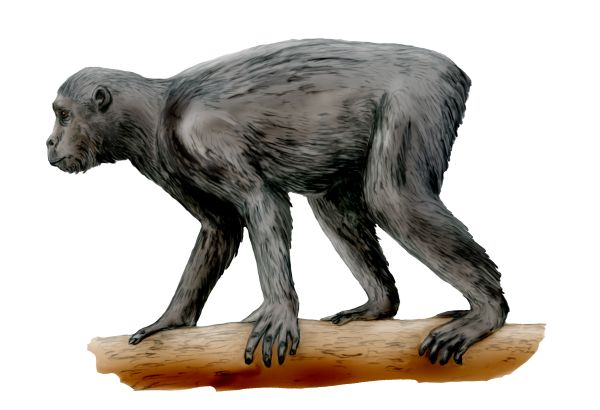
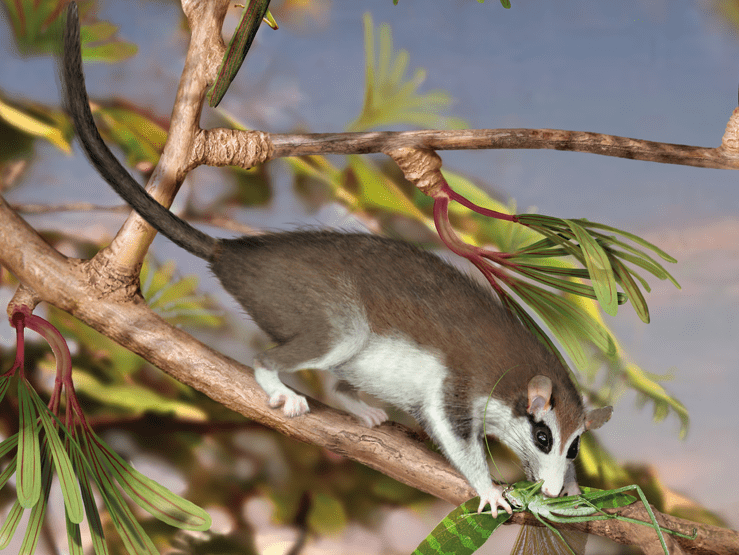
Opposable Thumb Emerges
Around 60 million years ago, the early ancestors of primates began to develop a crucial adaptation: the opposable thumb. This evolutionary milestone marked the beginning of increased dexterity and the ability to grasp objects more effectively. Living in the dense canopies of prehistoric forests, these early primates used their newly opposable thumbs to navigate their […]
Opposable Thumb Emerges Read More »