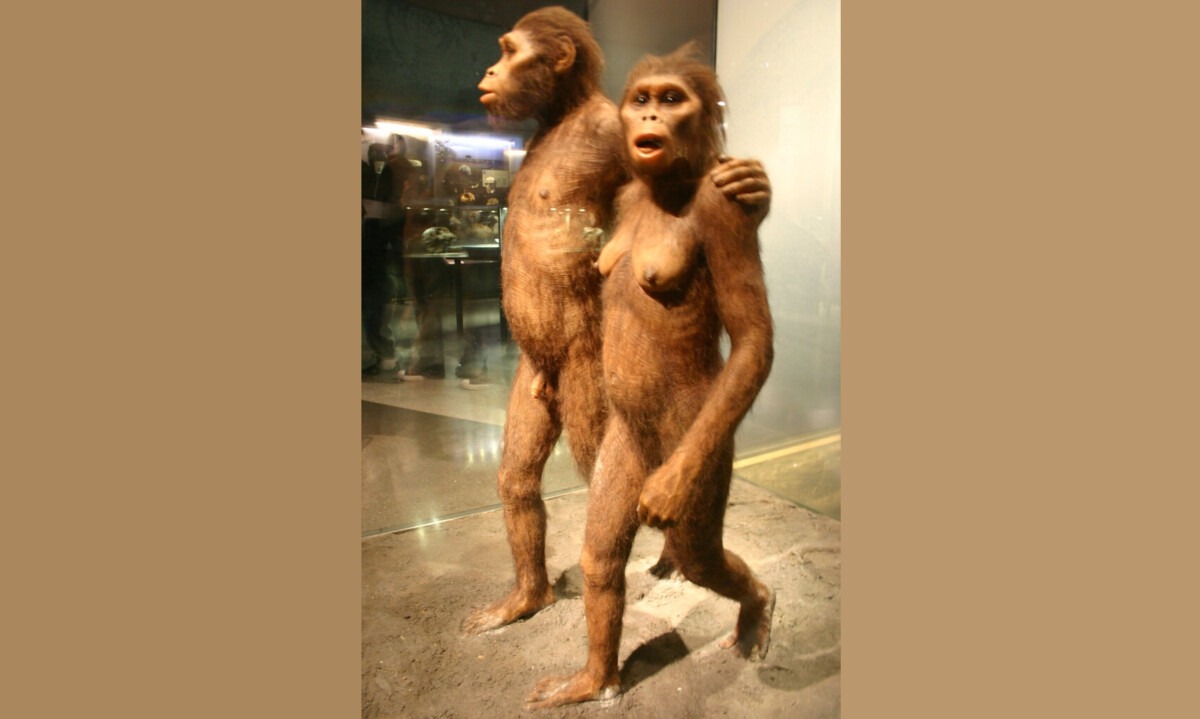
Genus: Australopithecus
116,000 Generations Ago This genus is more directly ancestral to humans and includes several species, such as Australopithecus afarensis (famously represented by “Lucy”), Australopithecus africanus, and others. Australopithecines show a greater commitment to bipedalism and have features more closely resembling modern humans, although they still retained some adaptations for climbing. This genus is known for […]
Genus: Australopithecus Read More »