Genus Orangutans
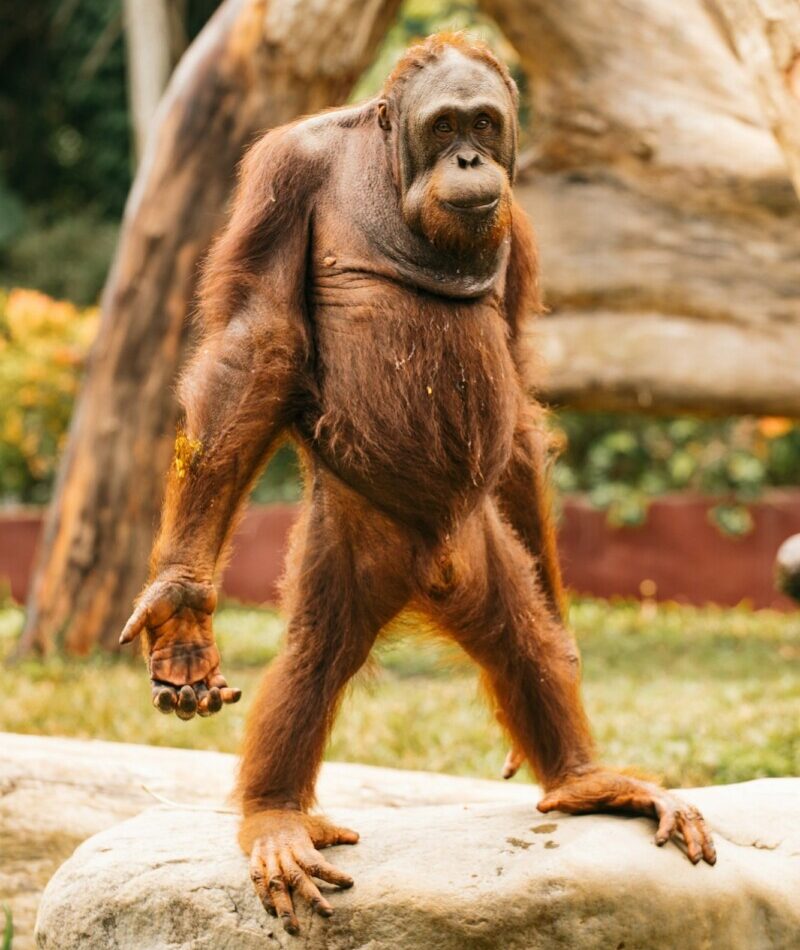
Orangutans (genus Pongo) are great apes native to Indonesia and Malaysia, characterized by their distinctive reddish-brown fur, long arms, and intelligent behavior. They are the most arboreal of all great apes, spending most of their time in trees, and are skilled climbers and swing between branches with ease. Orangutans are also known for their advanced […]