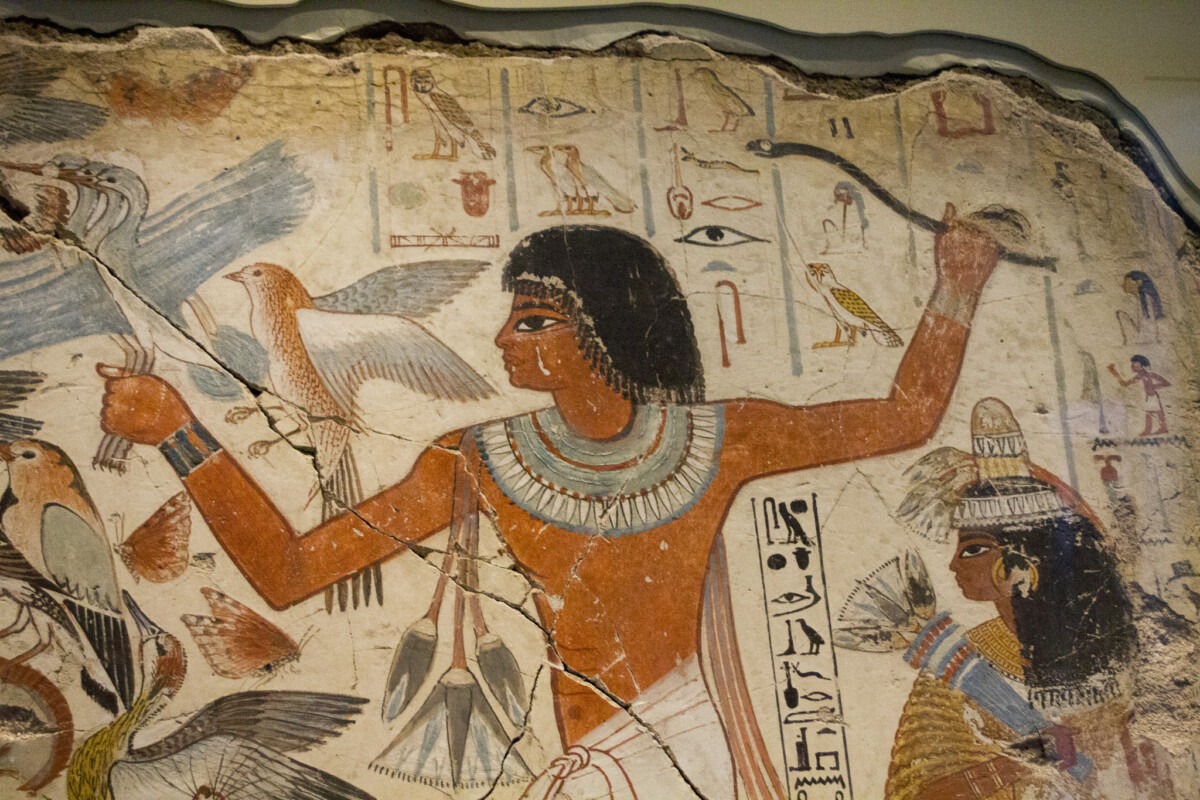
Frescoes of the Tomb of Nebamun
The Tomb of Nebamun, located in Thebes, Egypt, contains some of the most famous and vibrant frescoes from the 18th Dynasty of the New Kingdom period. The paintings depict Nebamun, an Egyptian official, engaging in various activities, including hunting in the marshes and enjoying banquets with his family. The frescoes are celebrated for their dynamic […]
Frescoes of the Tomb of Nebamun Read More »